本文将会通过TensorRT C++ API来完成一个MNIST手写数字识别模型的转换、推理过程,并给出相应代码,在runtime阶段将会使用最新的enqueueV3方法。
代码/模型文件已上传GitHub仓库:https://github.com/cyberyang123/Learning-TensorRT
图片来源:https://learnopencv.com/how-to-run-inference-using-tensorrt-c-api/
PyTorch模型搭建
这里搭建了一个简单的卷积网络,如果你在Windows系统上跑的话你可能需要将num_workers改成0
import torch
from torch import nn
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
# 这里为了简化runtime的步骤,不对图像进行归一化处理
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
train_data = datasets.MNIST(root = "./data/",
transform=transform,
train = True,
download = True)
test_data = datasets.MNIST(root="./data/",
transform = transform,
train = False)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data,batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,num_workers=2)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,num_workers=2)
import torch.nn.functional as F
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1,32,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32,64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64*7*7,1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024,512)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(512,10)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 7* 7)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = CNN()
import torch.optim as optim
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
net = net.to(device)
for epoch in range(20):
running_loss = 0.0
total_num, total_cor = 0,0
for i,data in enumerate(train_loader,0):#0是下标起始位置默认为0
#inputs,labels = data
inputs,labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
#初始为0,清除上个batch的梯度信息
optimizer.zero_grad()
#前向+后向+优化
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs,labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# loss 的输出,每个一百个batch输出,平均的loss
running_loss += loss.item()
if i%100 == 99:
print('[%d,%5d] loss :%.3f' %
(epoch+1,i+1,running_loss/100))
running_loss = 0.0
correct = 0
total = 0
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total = labels.size(0)# labels 的长度
total_num = total_num + total
correct = (predicted == labels).sum().item() # 预测正确的数目
total_cor = total_cor + correct
print("正确率:" + str(total_cor/total_num))
print('Finished Training')
PATH = './mnist_net.pt'
torch.save(net.state_dict(), PATH)
print('Saved Model')pt2onnx
这部分代码可以复用,换个模型也可以导出onnx,建议在导出的时候修改一下input、output层的命名。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1,32,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32,64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64*7*7,1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024,512)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(512,10)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 7* 7)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = CNN()
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('mnist_net.pt'))
net.eval()
torch_input = torch.randn(1, 1, 28, 28)
onnx_program = torch.onnx.export(net, torch_input, "MNIST.onnx", export_params=True)onnx2engine
从现在就开始C++的部分了,TensorRT从构建engine到推理的过程如下图所示:
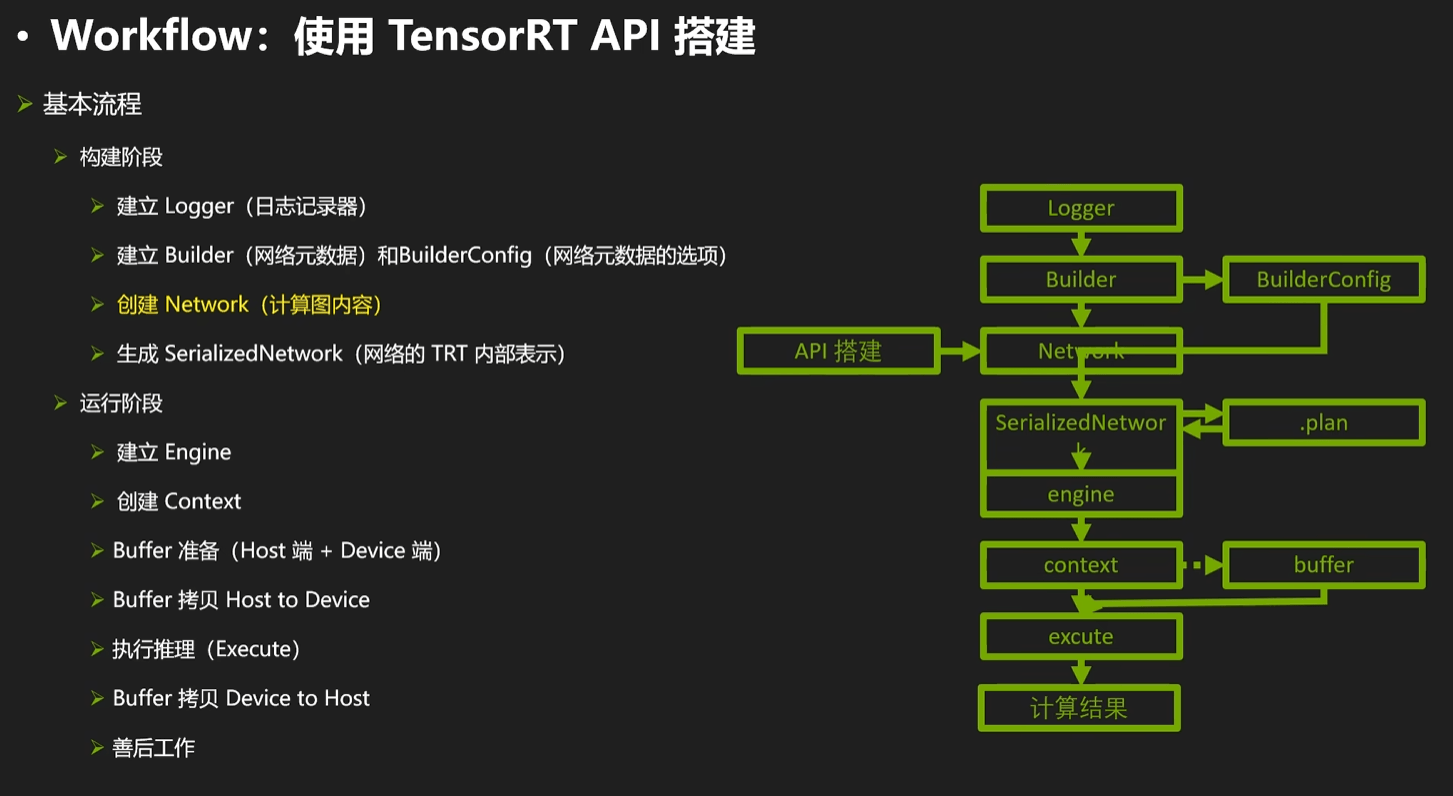
图片来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jj411Z7wG/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <assert.h>
#include <NvInfer.h>
#include <NvOnnxParser.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace nvinfer1;
// 以下示例捕获所有警告消息,但忽略信息性消息
class Logger : public ILogger
{
void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override
{
// 抑制信息级别的消息
if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING)
cout << msg << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 实例化ILogger
Logger logger;
// 创建builder
auto builder = unique_ptr<IBuilder>(createInferBuilder(logger));
// 创建网络(显性batch)
uint32_t flag = 1U <<static_cast<uint32_t>
(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH);
auto network = unique_ptr<INetworkDefinition>(builder->createNetworkV2(flag));
// 创建ONNX解析器:parser
auto parser = unique_ptr<nvonnxparser::IParser>(nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, logger));
// 读取文件
char *file_path = "MNIST.onnx";
parser->parseFromFile(file_path, static_cast<int32_t>(ILogger::Severity::kWARNING));
// 创建构建配置,用来指定trt如何优化模型
auto config = unique_ptr<IBuilderConfig>(builder->createBuilderConfig());
// 设定配置
// 工作空间大小
config->setMemoryPoolLimit(MemoryPoolType::kWORKSPACE, 1U << 20);
// 设置精度
config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16);
// 创建引擎
auto engine = unique_ptr<IHostMemory>(builder->buildSerializedNetwork(*network, *config));
//序列化保存engine
ofstream engine_file("./MNIST.engine", ios::binary);
assert(engine_file.is_open() && "Failed to open engine file");
engine_file.write((char *)engine->data(), engine->size());
engine_file.close();
cout << "Engine build success!" << endl;
return 0;
}智能指针真是个好东西,用完是不需要特意删除的
runtime
TensorRT有两个API可以执行推理,分别是execute()和enqueue(),区别在于前者是同步的,后者是异步的;enqueue()有3个版本,它们的区别可见下图,本文将使用最新的版本。

我从MNIST数据集里面取了10张照片放到了img文件夹下,用来测试推理。








#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <assert.h>
#include <NvInfer.h>
#include <NvOnnxParser.h>
#include <NvInferRuntime.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace nvinfer1;
// 以下示例捕获所有警告消息,但忽略信息性消息
class Logger : public ILogger
{
void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override
{
// 抑制信息级别的消息
if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING)
cout << msg << endl;
}
};
// 加载模型文件
std::vector<unsigned char> load_engine_file(const std::string &file_name)
{
std::vector<unsigned char> engine_data;
std::ifstream engine_file(file_name, std::ios::binary);
assert(engine_file.is_open() && "Unable to load engine file.");
engine_file.seekg(0, engine_file.end);
int length = engine_file.tellg();
engine_data.resize(length);
engine_file.seekg(0, engine_file.beg);
engine_file.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(engine_data.data()), length);
return engine_data;
}
int softmax(const float(&rst)[10]){
float cache = 0;
int idx = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i += 1)
{
if(rst[i]>cache)
{
cache = rst[i];
idx = i;
};
};
return idx;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 实例化ILogger
Logger logger;
// 创建runtime
auto runtime = unique_ptr<IRuntime>(createInferRuntime(logger));
// 读取engine,反序列化
string file_path = "MNIST.engine";
auto plan = load_engine_file(file_path);
auto engine = shared_ptr<ICudaEngine>(runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(plan.data(), plan.size()));
// 创建执行上下文
auto context = unique_ptr<IExecutionContext>(engine->createExecutionContext());
auto idims = engine->getTensorShape("input.1");// 这里的名字可以在导出时修改
auto odims = engine->getTensorShape("23");
Dims4 inputDims = { 1, idims.d[1], idims.d[2], idims.d[3] };
Dims2 outputDims = { 1, 10 };
context->setInputShape("input.1", inputDims);
void* buffers[2];
const int inputIndex = 0;
const int outputIndex = 1;
cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], 1 * 28 * 28 * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], 10 * sizeof(float));
// 设定数据地址
context->setTensorAddress("input.1", buffers[inputIndex]);
context->setTensorAddress("23", buffers[outputIndex]);
// 创建cuda流
cudaStream_t stream;
cudaStreamCreate(&stream);
// 读取文件执行推理
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i += 1)
{
// 读取图片
cv::Mat img0;
std::string file_name = "img/img" + std::to_string(i) + ".png";
img0 = cv::imread(file_name, 0);// 0为灰度图片
if (img0.empty()) //检测image有无数据,无数据 image.empty()返回 真
{
std::cout << "Could not open or find the image" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
cv::Mat img;
img0.convertTo(img, CV_32F);
// cv::imshow(file_name,img);
// cv::waitKey(0);
// 将图像拷贝到GPU
cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], img.data,1 * 28 * 28 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream);
//执行推理
context->enqueueV3(stream);
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
float rst[10];
cudaMemcpyAsync(&rst, buffers[outputIndex], 1 * 10 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);
cout << file_name << " 推理结果: " << softmax(rst) <<endl;
}
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]);
cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]);
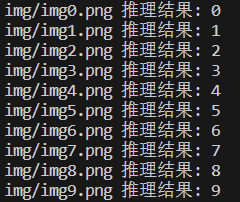
}成功得到结果
参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/112829371
https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/archives/index.html
https://www.dotndash.net/2023/03/09/using-tensorrt-with-opencv-cuda.html